Disposable Isolation Gown: A Shield of Protection
Material and Construction
Disposable isolation gowns are primarily crafted from non-woven materials such as polypropylene, polyethylene, or spunbond-meltblown-spunbond (SMS) fabric. These materials are chosen for their durability, fluid resistance, and breathability. The gowns are single-use, and their construction includes long sleeves, a front opening, and a tie-back closure, ensuring complete coverage of the wearer's body.
Purpose and Usage
The primary purpose of disposable isolation gown is to provide a barrier against potentially infectious materials and bodily fluids. Healthcare professionals commonly wear them during routine patient care activities, like examining patients, administering medications, or performing minor procedures that do not involve extensive fluid exposure. These gowns are designed to be discarded after each use, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
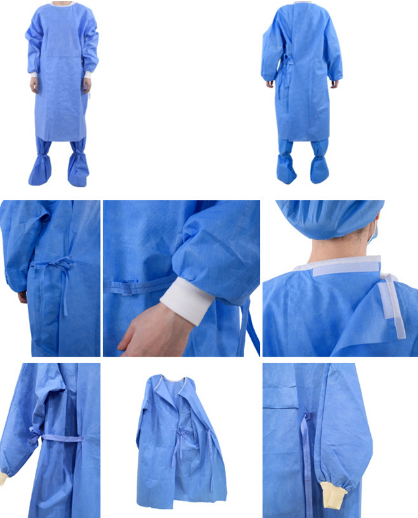
Key Features
Fluid Resistance: Disposable isolation gowns are engineered to repel liquids, safeguarding the wearer from contact with contaminants.
Comfort: Their lightweight and breathable design ensures comfort during prolonged wear, minimizing heat stress.
Cost-Efficiency: Being disposable, these gowns eliminate the need for laundering and sterilization, reducing operational costs.
Surgical Gown: Precision in the Operating Room
Material and Construction
Surgical gowns, on the other hand, are specifically tailored for use in sterile environments like operating rooms. They are typically made from tightly woven cotton or a blend of polyester and cotton, ensuring a high level of sterility. These gowns feature long sleeves and a wrap-around design, with closures at the back or front.
Purpose and Usage
Surgical gowns are a critical component of a surgeon's attire and serve the primary purpose of maintaining an aseptic environment during surgical procedures. Unlike disposable isolation gowns, surgical gowns are reusable and undergo strict sterilization processes, including autoclaving, to ensure they are free from microorganisms.
Key Features
Sterility: Surgical gowns are meticulously sterilized to prevent contamination in the operating room, minimizing the risk of surgical site infections.
Durability: These gowns are built to withstand multiple rounds of sterilization and provide long-lasting protection.
Customizability: Surgical gowns come in various sizes and styles to accommodate the diverse needs of surgical teams.
Key Differences: Disposable Isolation Gown vs. Surgical Gown
1. Purpose
Disposable isolation gowns are primarily intended to protect against contaminants and are disposed of after single use, while surgical gowns are designed to maintain sterility in surgical settings and can be reused.
2. Material
Disposable isolation gowns use non-woven materials for comfort and fluid resistance, whereas surgical gowns are crafted from tightly woven fabrics to ensure sterility.
3. Construction
Disposable isolation gowns typically feature a tie-back closure and front opening, whereas surgical gowns have wrap-around designs with various closure options.
Conclusion
In the medical world, understanding the fundamental differences between disposable isolation gowns and surgical gowns is paramount. Both serve critical roles in maintaining safety and hygiene, but they are tailored to specific medical scenarios. While disposable isolation gowns offer cost-effective protection against contaminants in non-sterile environments, surgical gowns are the guardians of sterility in the operating room.
Ultimately, the choice between these two garments depends on the healthcare setting and the specific requirements of the task at hand. By recognizing their unique characteristics and purposes, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions to ensure the well-being of both themselves and their patients.





Comments
0